Skin xenograft hcmv megan loydor studying skin physiology but also for advancing treatments for various dermatological conditions. However, one of the primary challenges in this area is managing human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection, which can complicate the xenograft process and affect the research outcomes.
In this context, Megan Loyd’s groundbreaking study has been instrumental in examining the interaction between HCMV and skin xenografts. Her research offers essential insights into the virus’s impact on graft integrity and immune responses, laying the foundation for more effective control strategies and advancing the use of xenografts in medical research. Loyd’s contributions are widely recognized for enhancing the understanding and application of xenografts, providing a roadmap for safer and more effective use in experimental and therapeutic contexts.
What Is A Skin Xenograft?
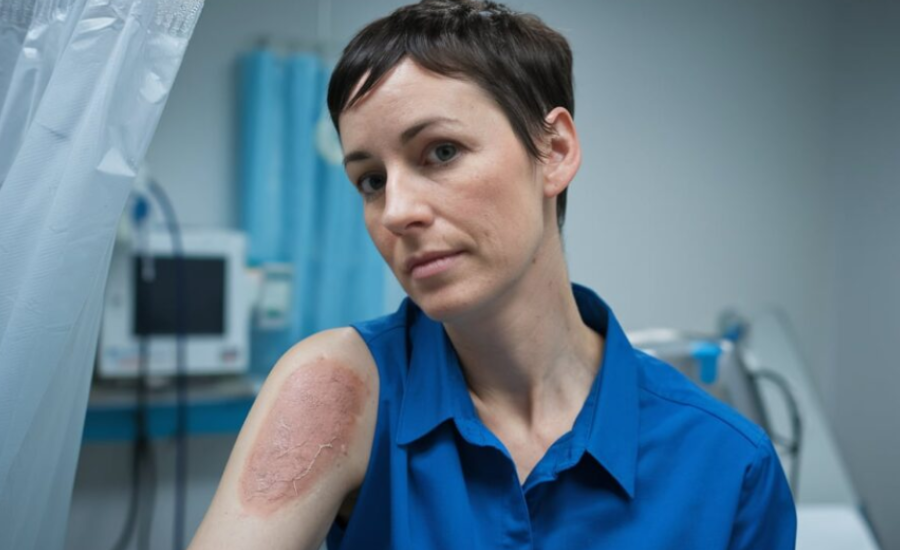
Transplanting skin tissue from animals to humans, a process known as xenografting, represents a critical advancement in medical research. This technique allows scientists to observe human-like skin responses in ways that traditional models cannot replicate, offering a unique framework for studying immune reactions, skin conditions, and potential therapies. By using animal-derived skin in research, xenografts provide detailed insights into human skin biology, which helps to bridge gaps in understanding that other research models leave open.
In addition to its role in skin studies, xenografting is particularly valuable for researching viral diseases and assessing drug responses. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection, for instance, is one of the main challenges in xenograft research, as it can impact the success and longevity of the transplant. Studying HCMV in the context of xenografts not only advances knowledge about the virus’s effects on transplanted tissues but also aids in developing more effective antiviral treatments, helping to make xenografts a safer and more reliable tool in experimental medicine.
Skin Xenografts: Significance For Research
Skin xenograft hcmv megan loyd, particularly in research on human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), are powerful tools for advancing our understanding of the human immune system, tissue regeneration, and the effects of viral infections on transplanted tissues. By using xenografts to simulate human skin in a controlled lab environment, scientists can closely examine how human skin responds to various therapies and infections, offering insights that are otherwise challenging to achieve in traditional models. This method, pioneered in part by researchers like Megan Loyd, opens doors to discovering effective treatments and preventive measures against complications in skin transplants.
The findings from studies involving skin xenografts are crucial not only for enhancing success rates in medical transplants but also for developing targeted therapies for a range of skin-related conditions. Through this research, scientists are building a foundation for treatments that may improve patient outcomes by reducing rejection risks and managing infections like HCMV. The advancements driven by these studies underscore the importance of xenografting in medical research, as it continues to provide valuable knowledge to support safer and more effective transplantation techniques.
Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV): A Problem With Xenografts
In skin xenograft hcmv megan loyd, managing human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is crucial due to the virus’s potential to disrupt transplanted tissues significantly. As a member of the herpesvirus family, HCMV poses serious risks to the success of xenografts, potentially leading to graft rejection and other negative outcomes. When HCMV infects transplanted tissues, it can provoke immune complications, making it harder for the recipient’s body to accept the new skin tissue.
The immune challenges presented by HCMV extend beyond simple infection, as the virus is known to weaken immune responses, further complicating the integration of foreign tissues or organs. This highlights the importance of understanding HCMV’s role in xenograft outcomes. Developing treatments to counteract the virus’s effects on skin xenografts is essential for improving transplant success rates and minimizing complications, paving the way for more effective and resilient approaches to tissue and organ transplantation.
The Impact Of Megan Loyd On Xenograft Research
Megan Loyd has made notable contributions to the field of skin xenografts, particularly in exploring how human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) impacts these procedures. Her research delves into understanding the mechanisms by which HCMV affects transplanted skin tissues, uncovering factors that can compromise the success of xenografts. Loyd’s work emphasizes finding ways to mitigate these viral impacts, which has significant implications for improving the integration and longevity of transplanted skin tissues in clinical settings.
Through her studies, Loyd has provided valuable insights that could lead to higher success rates for skin xenografts, especially when used to treat severe skin conditions. Her findings support advancements in making xenografts more resilient and adaptable for therapeutic applications, highlighting their potential as viable treatments for patients facing critical skin injuries and disorders.
HCMV Mechanisms In Skin Xenografts
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) exerts a complex influence on skin xenografts, affecting them through various pathways. One way it interferes is through direct cytopathic effects, causing cell damage in the transplanted tissue itself. Additionally, HCMV can trigger significant inflammation in the grafted area, creating an environment that hinders the healing process and raises the risk of transplant rejection. This viral irritation in the transplant site can complicate the patient’s recovery, making management of these effects essential.
Another critical aspect of HCMV’s impact is its ability to manipulate immune responses, especially by altering the expression of immune-related genes within the transplanted skin. By interfering with these genetic pathways, HCMV increases the likelihood of immune rejection, as the host’s immune system may more readily target the foreign tissue. Understanding these specific mechanisms is crucial for developing strategies to counter HCMV’s negative effects on skin xenografts, paving the way for more resilient and compatible transplant outcomes.
Methods For Fighting HCMV In Xenografts
Researchers, including Megan Loyd, are uncovering ways to enhance the success of skin xenografts, particularly by addressing challenges posed by human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). One promising avenue is the use of antiviral medications, which can target HCMV directly and potentially reduce its detrimental effects on transplanted skin tissues. These treatments could improve graft viability, allowing for better integration and minimizing the risk of rejection.
In addition to antiviral therapies, advanced gene-editing strategies are being explored to make donor skin tissues more resistant to HCMV. By modifying specific genes within the grafted tissue, scientists aim to strengthen its defenses against viral infection. Together, these approaches—combining antiviral drugs with genetic enhancements—could significantly mitigate the impact of HCMV on skin xenografts, leading to improved patient outcomes and offering more reliable options for treating complex skin conditions.
Immunosuppression’s Function In Skin Xenografts
Immunosuppression plays a crucial role in the success of skin xenograft hcmv megan loyd, as it helps to prevent the recipient’s immune system from attacking and rejecting the transplanted tissue. However, the use of immunosuppressive medications also brings added risks, notably an increased susceptibility to infections like human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). Balancing this suppression is essential, as researchers strive to find an optimal level that will safeguard the graft while minimizing infection risk.
Current studies are focused on understanding the fine line between sufficient immunosuppression to avoid graft rejection and maintaining enough immune function to defend against pathogens. By exploring this balance, researchers, including Megan Loyd, hope to improve outcomes for patients undergoing xenograft procedures, creating a safer approach that prevents both rejection and severe infections. This research is critical to advancing treatments in skin xenotransplantation, with the potential to make these procedures more effective and widely accessible.
Technological Developments In Xenografts
The field of skin xenograft hcmv megan loyd has seen significant progress with advancements in technology, which have greatly improved the accuracy and safety of these procedures. Techniques like 3D bioprinting allow for precise layering of skin cells, enabling researchers to create grafts that closely resemble human skin. This innovation reduces the likelihood of complications and enhances the graft’s compatibility with the host. Additionally, CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing offers a powerful tool to modify donor cells, making them less likely to trigger immune rejection or be susceptible to infections like HCMV.
These advancements are paving the way for more effective skin transplantation in the future. By refining methods and reducing associated risks, researchers aim to broaden the applications of skin xenografts. The hope is that these technologies will eventually lead to successful, long-lasting outcomes in patients with severe skin injuries or conditions, significantly expanding treatment possibilities and enhancing patient recovery experiences.
The Prospects For Skin Allografts
The future of skin xenograft hcmv megan loyd is promising, with researchers like Megan Loyd paving the way for groundbreaking advancements. Her contributions offer crucial insights into the cellular processes and immune interactions involved in xenografts, potentially transforming the application of skin implants. Loyd’s work provides a strong foundation for understanding how to improve the integration and effectiveness of xenografts, which can significantly enhance treatment options for patients.
As scientists explore new technologies, such as advanced gene editing and bioprinting techniques, skin xenografts are moving closer to becoming a reliable treatment for severe injuries and chronic skin conditions. The ongoing research efforts are creating a roadmap for making these procedures safer, more accessible, and effective in clinical settings, bringing hope to many in need of restorative skin therapies.
Skin Xenografts: Clinical Uses And Applications
Skin xenografts have a wide range of applications in clinical settings, particularly for managing complex skin conditions that do not respond to conventional treatments, as well as for treating burns and open wounds. By utilizing xenografts, physicians can offer patients a temporary skin covering while they await a suitable human donor or as their own skin heals. This approach not only aids in wound healing but also helps protect the underlying tissue from infection and environmental exposure.
However, for skin xenograft hcmv megan loyd to be used effectively in therapeutic contexts, addressing complications such as human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection is crucial. Understanding and managing these side effects is essential to improving patient outcomes and ensuring the success of skin transplantation procedures. Continued research in this area will be vital for refining xenograft applications, enhancing their safety, and expanding their use in treating various skin-related conditions.
Ethics In Skin Xenografts: A Consideration
The use of skin xenografts, while promising in advancing medical treatments, inevitably raises ethical considerations that cannot be overlooked. One of the primary concerns involves the use of animal tissues in human medicine, which prompts questions about the moral implications of sourcing these tissues. Additionally, there are worries about the potential risks that patients might face, including adverse reactions and the long-term consequences of using transgenic tissues. These ethical dilemmas necessitate careful consideration and dialogue within the medical community to ensure that patient welfare is prioritized.
Researchers like Megan Loyd and her team are acutely aware of these ethical challenges and are committed to addressing them responsibly. Their dedication to adhering to stringent ethical guidelines underscores the importance of conducting research that prioritizes both safety and integrity. By implementing robust ethical frameworks, they aim to ensure that their findings contribute positively to the field of xenotransplantation, while also fostering public trust in this innovative area of medical science. Their work serves as a reminder that scientific advancement must always be accompanied by a strong commitment to ethical responsibility.
1Views Of Patients Concerning Skin Xenografts
Patients undergoing skin xenograft procedures often face a range of psychological and physical challenges that can significantly impact their overall well-being. Understanding their perspectives is crucial for improving the outcomes and experiences associated with these surgeries. By gathering insights directly from patients, researchers and medical professionals can identify the specific emotional and physical hurdles they encounter. This knowledge is essential not only for enhancing the technical aspects of xenograft procedures but also for ensuring that patients receive the necessary support throughout their treatment journey.
Additionally, addressing these challenges involves a holistic approach that encompasses both the medical and psychological aspects of care. Providing comprehensive support services, such as counseling and peer support groups, can greatly benefit patients as they navigate the complexities of their treatment. By prioritizing patient experiences and fostering open communication, healthcare providers can create a more supportive environment that empowers individuals during their recovery process. This commitment to understanding and addressing the multifaceted difficulties faced by skin xenograft patients ultimately contributes to better care and improved long-term outcomes.
Knowledge And Understanding In Xenograft Research
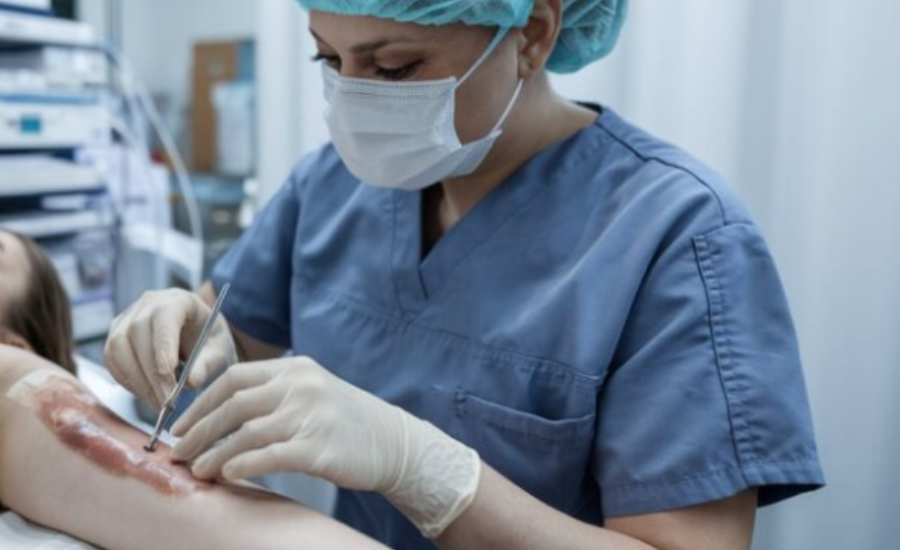
Raising awareness among the public, patients, and healthcare professionals about the potential benefits and challenges associated with skin xenografts, particularly in relation to human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), is vital for the advancement of this field. Megan Loyd has emerged as a passionate advocate for increasing visibility into research on xenografts, emphasizing the importance of informed decision-making and the ethical considerations involved. Her contributions have sparked meaningful discussions within the medical community, shedding light on the complexities of skin xenograft procedures and their implications for patient care.
Collaboration among scientists, healthcare providers, and industry partners is essential for the continued development of effective skin xenograft strategies. Through cooperative efforts, these stakeholders can share resources, technologies, and expertise to address the challenges posed by HCMV and other related issues. Megan Loyd has taken a leadership role in promoting interdisciplinary collaboration, recognizing that this field requires diverse perspectives to achieve the best possible outcomes for patients. By fostering a unified approach, the research community can enhance the efficacy of skin xenograft procedures, ultimately improving patient care and success rates in treating complex skin conditions.
FAQs
Q: What is a skin xenograft?
A: A skin xenograft is a transplant procedure where skin tissue is taken from one species and implanted into another. This technique is primarily used in research to study immune responses and skin diseases, allowing scientists to investigate treatments in a way that traditional models cannot.
Q: How are skin xenografts used in research?
A: Skin xenografts are valuable for exploring various skin conditions and immune reactions. They enable researchers to observe how human skin responds to infections and therapies, which can inform better management of skin diseases and improve transplant success rates.
Q: What role does human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) play in xenografts?
A: HCMV poses challenges for skin xenografts as it can impair immune responses, leading to graft rejection or other complications. Understanding how HCMV affects graft acceptance is crucial for improving the success of these transplants.
Conclusion
The field of skin xenografts is advancing rapidly, driven by researchers like Megan Loyd who are addressing the challenges posed by human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and improving graft survival rates. With developments in gene editing, immunosuppressive strategies, and antiviral treatments, skin xenograft hcmv megan loyd are becoming a more promising option for treating severe skin conditions and injuries. This ongoing research not only enhances patient outcomes but also deepens our understanding of immune responses and viral behaviors in transplanted tissues, paving the way for revolutionary treatment options when traditional therapies are inadequate.
Stay in touch for more updates and alerts visit: Cofee Manga!
